Wenn wir an Cyberangriffe auf kritische Infrastrukturen denken, stehen oft Ransomware-Kampagnen oder staatlich gesponserte Angriffe auf industrielle Kontrollsysteme im Mittelpunkt. Doch einige der effektivsten Angriffe beginnen nicht mit einem ausgeklügelten Exploit. Sie beginnen mit einer Datei.
Was ist ein File-Bourne-Angriff in einer IT-OT-Umgebung?
Dateiübertragende Angriffe sind ein wachsender Bedrohungsvektor, der die Bewegung von Dateien zwischen IT- und OT-Netzwerken ausnutzt, um Malware in kritische Infrastrukturen einzuschleusen. In modernen konvergierten IT-OT-Umgebungen tritt ein File-Bourne-Angriff auf, wenn eine bösartige Datei von einem IT-Unternehmensnetzwerk in eine OT-Umgebung (Betriebstechnologie) gelangt. Dort angekommen, kann sie die Produktion stören, Ausfallzeiten verursachen oder sensible Prozesse gefährden.
Da die IT-OT-Integration und die Remote-Konnektivität die Angriffsfläche vergrößern, ist die Sicherung des Dateiverkehrs für die Verteidiger kritischer Infrastrukturen zur obersten Priorität geworden.
Die Bedrohung der kritischen Infrastruktur
Kritische Vorgänge hängen von Dateiübertragungen für Software-Updates, Lieferantenlieferungen, technische Zeichnungen und Sensordaten ab. Leider werden diese vertrauenswürdigen Dateiaustausche zunehmend als Vehikel für Malware genutzt.
Die Angreifer nutzen gängige Dateiübertragungswege aus:
- USB und Laptops, die von Auftragnehmern oder Mitarbeitern mitgeführt werden
- Gemeinsamer Cloud-Speicher zur Synchronisierung von Dateien in OT-Umgebungen
- E-Mail-Anhänge, die an herkömmlichen Filtern vorbeigehen
- Nicht verwaltete Dateitransfer-Workflows zwischen Geschäfts- und Betriebsbereichen
Laut SANS gaben 27 % der ICS-Sicherheitsexperten an, dass flüchtige Geräte wie USBs zu den wichtigsten Malware-Infektionsvektoren in der OT gehören, während 33 % der ICS-Vorfälle von Geräten mit Internetzugang und Remote-Diensten ausgehen. Die Beweise sind eindeutig: IT-OT-Datenströme gehören zu den am stärksten gefährdeten Pfaden in der modernen Infrastruktur.
Wie ein dateibasierter Angriff funktioniert
Ein typischer dateibasierter Angriff bewegt sich Schritt für Schritt von der IT in die OT:
- Eingebettete Nutzlast: Malware wird in einer legitim aussehenden Datei versteckt, z. B. in einer PDF-Datei, einem Update-Paket oder einer technischen Projektdatei.
- Die Datei hat ihren Ursprung in der IT: Sie gelangt über E-Mail, ein Lieferantenportal oder ein Cloud-Collaboration-Tool in das Unternehmen.
- Übertragung von der IT in die OT: Die Datei gelangt über eine Netzwerkbrücke, einen Wechseldatenträger oder sogar eine Datendiode in die OT, wenn sie nicht ordnungsgemäß inspiziert wird.
- Ausführung im OT: Sobald die Malware geöffnet oder ausgeführt wird, explodiert sie und stört den Betrieb oder ermöglicht Datendiebstahl.

Parallelen zur realen Welt:
- Stuxnet verbreitete sich über infizierte USB , die Luftlöcher umgingen.
- TRITON wurde über bösartige technische Dateien verbreitet.
- Die Ausnutzung von MOVEit zeigte, wie Dateiübertragungssysteme selbst zu einem direkten Ziel werden können.
In jedem Fall hätte ein mehrstufiger sicherer Dateiübertragungsprozess die bösartige Nutzlast neutralisieren, Null-Vertrauensrichtlinien durchsetzen und sicherstellen können, dass die Dateien vor dem Eintritt in kritische Systeme bereinigt werden.
Auswirkungen auf kritische Infrastrukturen
Wenn bösartige Dateien von der IT in die OT gelangen, gehen die Folgen weit über den digitalen Schaden hinaus:
- Betriebsbedingte Ausfallzeiten: Angehaltene Produktionslinien, unterbrochene Dienste, Ausfälle.
- Physische Schäden und Sicherheitsrisiken: Manipulierte Kontrollen oder fehlerhafte Updates können Menschenleben gefährden.
- Verstöße gegen die Vorschriften: Die Nichteinhaltung von NIST-, NIS2-, HIPAA- oder PCI-Vorschriften kann zu Bußgeldern und Lizenzproblemen führen.
- Reputationsschaden: Verlust des Vertrauens von Kunden und Partnern nach einem öffentlichen Vorfall.
Angesichts der Tatsache, dass 76 % der Industrieunternehmen von Cyberangriffen in OT-Umgebungen berichten (ABI/Palo Alto, 2024), besteht dringender Bedarf an widerstandsfähigen Schutzmaßnahmen.
Verteidigungsstrategien für IT-OT-Dateiflüsse
Um Angriffe auf Dateien zu stoppen, bedarf es mehr als einer verschlüsselten Übertragung. Eine Schutzschicht muss direkt in jede Übertragung eingebettet werden. Zu den wichtigsten Strategien gehören:
- Mehrschichtige Inspektion: OPSWAT wie Metascan™ Multiscanning, Deep CDR™, Adaptive Sandbox und File-Based Vulnerability Assessment erkennen, entschärfen oder entschärfen bösartige Dateien, bevor sie in OT gelangen.
- Zero-Trust-Durchsetzung: RBAC (rollenbasierte Zugriffskontrolle), aufsichtsrechtliche Genehmigungen und richtliniengesteuerte Workflows verhindern unbefugte oder nicht genehmigte Übertragungen.
- Kontrolle und Sichtbarkeit: Unveränderliche Prüfpfade und zentralisierte Dashboards sorgen für Übersicht und Konformitätssicherheit.
Wie die OPSWAT dies leistet:
- MetaDefender Managed File Transfer MFT)™ automatisiert sichere, kontrollierte Dateiübertragungen zwischen IT, OT und Cloud.
- MetaDefender Kiosk™ säubert Dateien von USB-Sticks, Laptops und Auftragnehmern, bevor sie in sensible Netzwerke gelangen.
- MetaDefender NetWall® Data Diode erzwingt unidirektionale, richtliniengesteuerte Übertragungen, um OT vor eingehenden Bedrohungen zu schützen.
Gemeinsam schaffen diese Lösungen einen sicheren Übertragungsweg, der sicherstellt, dass jede Datei überprüft, bereinigt und kontrolliert wird, bevor sie die Domänengrenzen überschreitet.
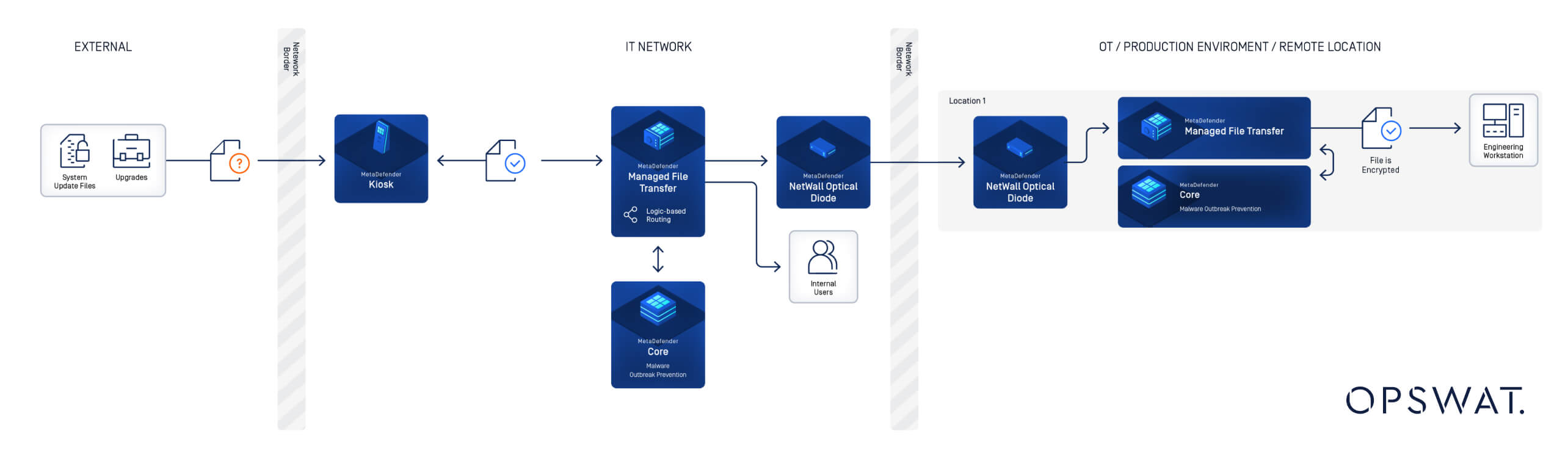
Praktische Lektionen aus dateibasierten Angriffen
- Infizierte USB können von MetaDefender Kiosk durch Bereinigung und Richtliniendurchsetzung blockiert werden, bevor sie OT-Anlagen erreichen.
- Engineering-Workstation-Dateien aus weniger vertrauenswürdigen Quellen werden von MetaDefender Managed File Transfer MFT) überprüft und unterliegen der Durchsetzung von Richtlinien, um bösartige oder nicht konforme Inhalte zu blockieren, bevor sie die Sicherheitssysteme erreichen.
- Die Nutzung von MFT zeigt, dass eine mehrschichtige Prüfung, die Durchsetzung von Richtlinien und eine überprüfbare Verwaltung in Dateiübertragungslösungen integriert werden müssen.
Jeder Fall unterstreicht den gleichen Punkt: Eine stabile Dateiübertragung ist nicht optional, sondern unerlässlich.
Nächste Schritte: Resilienz auf der Dateiebene aufbauen
Dateibasierte Angriffe werden sich mit der Konvergenz von IT- und OT-Netzwerken weiterentwickeln. Die effektivste Verteidigung besteht darin, jede Datei über jeden Vektor zu sichern, unabhängig davon, ob sie sich über das Netzwerk, über Domänengrenzen oder über transiente Geräte bewegt.
Laden Sie das eBook Resilienz neu definieren mit Secure MFT herunter
Entdecken Sie Fallstudien, tiefe technische Einblicke und die vollständige Checkliste für eine sichere Dateiübertragung.
Sind Sie bereit, Managed File Transfer führendeMetaDefender Managed File Transfer MFT) -Lösung OPSWAT mit maßgeschneiderten Lösungen für Ihre bestehende Infrastruktur zu integrieren?

